Faster RCNN作为经典的两阶段目标检测算法,实现细节超多,不太好理解. 花了好久终于把代码理清楚了,这里特别感谢@陈云 大佬的 simple-faster-rcnn-pytorch 项目,代码简洁易懂,非常适合学习. 也参考了 @BBuf 的代码解析 以及 tryo labs 的tutorial. 参考图片部分均会指明(@tryolabs 部分居多).
论到目标检测, 一个很自然的想法就是直接在图片上划分某些区域, 然后判断这些区域是否为 (或含有) object部分. RCNN就是沿着这种朴素的思路发展而来的. 个人认为从RCNN到Faster RCNN最为重要的就是候选区域(Proposal)的生成, 从原始的图像分割到基于anchor, 速度也越来越快. 如何理解呢?

我们这里粗略理解为使用滑动框在图片上以一定的步长滑动, 然后得到若干区域(Proposal), 将这些区域送入第一层分类器判断是否含有物体, 过滤没有物体的部分并合并重叠区域较多的部分(ROI), 然后再送入第二层分类器判断物体类别. 简单讲RCNN系列就是这个思路. RCNN到FasterRCNN中区别最大的就是这个Proposal生成的方法.
整体结构
我们先从宏观上看一下整体网络结构. 之后再深入各个部分的细节研究.
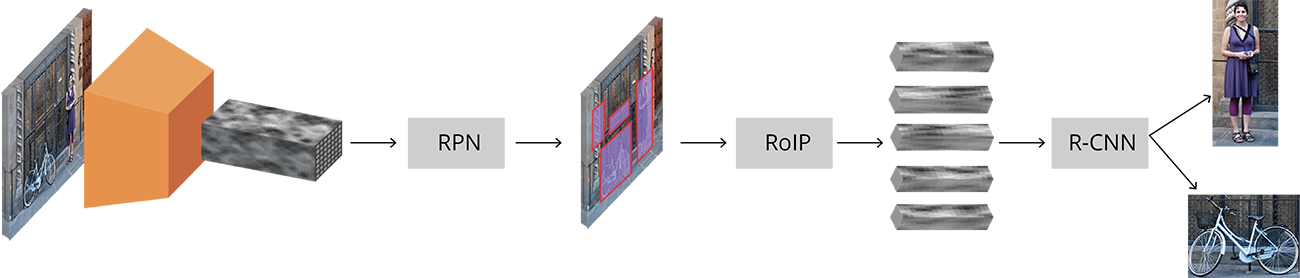
- 图片送入预训练好的骨干网络(VGG)中得到特征图
- 特征图首先进入RPN(region proposal network)网络生成候选区域(proposal)
- 候选区域结合特征图送入ROIPooling中获得归一化的特征
- 将特征送入R-CNN网络进行分类与回归, 获得结果
下面我们一步步理清楚各个组件的构造.
骨干网络
使用预训练好的骨干网络提取特征很简单. 原文使用在 ImageNet 上预训练的VGG . 由于速度及部署等原因, 也有人使用 MobileNet 的. 现在各种网络层出不穷, 究竟使用什么网络也是一个很有 trick的工作.
VGG

VGG, 来源于2014年ImageNet ILSVRC竞赛(Karen Simonyan & Andrew Zisserman). 224*224*3的RGB图片 (必须固定大小, 因为最后使用全连接层来进行分类) 送入网络, 最后卷积层的输出被全连接层展开成1*1*1000的大小后送入softmax进行分类.
代码中使用了 conv5层的卷积层的输出作为特诊图. 最后的特征图变为 14*14*512的形状.

Anchors
怎么在特诊图上找出合适的候选区域呢(Proposal)?我们看到图1的滑动窗, 这样来获取固定大小的候选框很简单. 那滑动窗如何设置呢?毕竟图片上的物体往往是不同大小的. Faster-RCNN采用9种不同尺寸的滑动窗来采集Proposal (不严谨的比喻啦) . 大小为 width*height*depth 的 feature map 上可产生 width*height*9 个anchor. 形象地理解, 每个depth维的feature map上的点集数据为9个anchor提供分类及回归的数据来源.
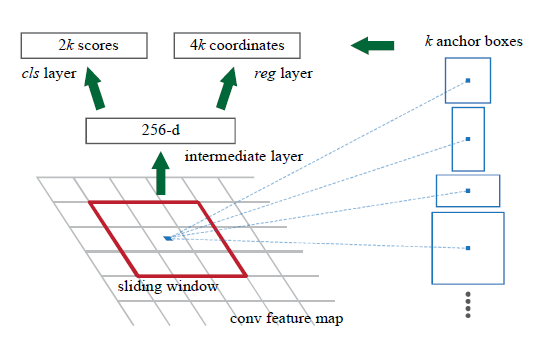
上图中形象地展示了一个 256-d的feature map点代表了原图9个不同 anchor. 我们知道, 原图经过多次卷积、降采样后得到 feature map , feature map尺寸相比原图缩小了$2^r$倍(r是降采样率), 如果我们把 anchor 中心映射回原图, 将得到如下图片:

Region Proposal Network

继续下去, RPN 接收 feature map输出一系列目标 proposal. RPN 网络对每个 anchor 有两个输出. 1. 其中一个是 anchor 的属于物体前景的概率(不关心是哪类物体). 这将为下面第二阶段 (RCNN 识别具体物体类别) 过滤不属于物体前景的 anchor ;2. 另一个输出是物体框(bbox)回归, 也就是 anchor 相对物体的位置偏移.
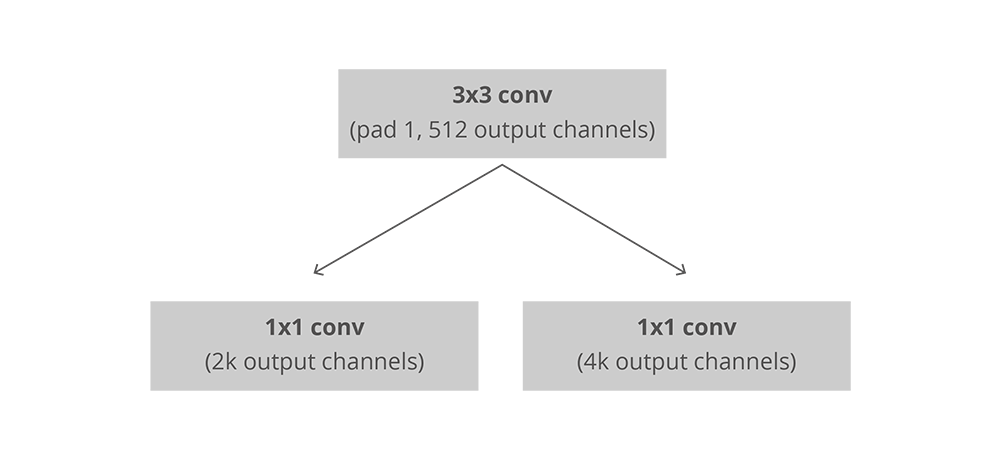
RPN 使用过全卷积方式来实现的. 它接受骨干网络传来的特征图(feature map). 上图已经解释的很清楚了:首先让feature map通过512通道的 3x3 卷积, 然后分为两支;均为1x1的卷积. 对于分类层, 输出每个 anchor 属于前景/背景的分数;回归层, 输出 anchor 相对物体的偏移: $Δ_{x_{center}},Δ_{y_{center}},Δ_{width},Δ_{height}$ .
损失函数
训练阶段, 将图片中的 anchor 分为两类(严格意义上是三类). 与物体 IoU 大于0.5的 anchor 被认为是前景类;与物体完全没有重叠或者 IoU 小于0.1的被认为是背景类. 其余的 anchor 不参与计算损失. 之后从前景类与背景类 anchor 中以一定比例随机采样256个进入训练.
RPN使用 二分类交叉熵 来计算选中 anchor 的分类损失. 对于回归损失, 我们仅使用前景类 anchor 和最近的前景来计算损失(背景类肯定不能计算啊). 文章使用 Smooth L1 损失.
后处理
Non-Maximum suppression 非极大值抑制. 很多 anchor 都有重叠, 提出的 proposal 也在很多物体上有重叠. 我们使用极大值抑制(NMS)来解决这个问题. NMS 将一系列proposal按得分情况排序, 合并两个IOU值在阈值之上的proposals为一个, 然后再次迭代地重复这个过程. 这个重叠IoU阈值很关键, 太低的话会导致错过很多 proposal;太高的话会导致同一物体有太多 proposal. 常用的阈值是 0.6.
Region of Interest Pooling
经过RPN这一步后, 有了大量的物体 候选区域( object proposals). 下一个问题就是如何将它们正确分类了.
最简单的方式就是直接把这些proposals裁剪然后放入预训练的分类骨干网络进行分类. 可以使用提取到的 feature map 作为图片分类器的输入. 这里有个问题:近2000个proposals要进行计算, 这会非常的慢且低效.
Faster R-CNN重新使用已经存在的 feature map来尝试去解决这个问题:可以对每个 proposal提取对应的固定大小的 feature map . R-CNN接受固定大小的 feature map 来分类到指定的类别.

实现中是将proposal对应的feature map部分裁剪出来, 然后 resize 到固定大小.
Region-based Convolutional Neural Network
Region-based Convolutional Neural Network(R-CNN)是Faster R-CNN 最后的一步. 从图中得到特征图后, 使用它通过 RPN 得到物体候选(object proposal), 并通过 RoI Pooling 提取每个 proposal的特征, 并将这些特征用来做最后的分类. R-CNN有两个目标:
-
将proposals分类为某一类别.
-
调整proposal的位置
在原始 Faster R-CNN文章中, R-CNN接受每个 proposal的 feature map 并使用两个4096维的全连接层来将特征展开(flatten?).
之后它使用两个不同的全连接层来讲每个 object 进行分类与回归:
-
N+1个分类结果的全连接层. N是物体类别, 加上1表示背景类.
-
4N个回归结果的全连接层. 需要对N个可能的物体预测四个回归位置: $Δ_{x_{center}},Δ_{y_{center}},Δ_{width},Δ_{height}$ .

代码详解
Talk is cheap, show me the code. 说了这么多, 可能还是有个粗略的概念. 我们直接来上代码看一看. 这里参考@陈云 大佬的 simple-faster-rcnn-pytorch 项目.
整体架构已经了解了:

就像我们上面所说的, 两个阶段清晰明了. 我们这里尝试从宏观到细微, 一步步来探究 整个工程 的细节.
工程目录
点击显示: 整体目录
```bash ├── LICENSE ├── README.MD ├── data │ ├── __init__.py │ ├── dataset.py │ ├── util.py │ └── voc_dataset.py ├── demo.ipynb ├── misc │ ├── convert_caffe_pretrain.py │ ├── demo.jpg │ └── train_fast.py ├── model │ ├── __init__.py │ ├── faster_rcnn.py │ ├── faster_rcnn_vgg16.py │ ├── region_proposal_network.py │ └── utils │ ├── __init__.py │ ├── bbox_tools.py │ └── creator_tool.py ├── requirements.txt ├── train.py ├── trainer.py ├── tree.txt └── utils ├── __init__.py ├── array_tool.py ├── config.py ├── eval_tool.py └── vis_tool.py ```看起来有些庞大, 我们先了解一下代码大致架构 (红色框体 AnchorTargetCreator 和 ProposalTargetCreator仅在训练过程中出现) .
train.py
我们需要找个入口来一步步深入. 就从经典的 train.py开始吧.
点击显示: train_py
``` def train(**kwargs): opt._parse(kwargs) dataset = Dataset(opt) print('load data') # 用 VOCBboxDataset 作为数据集, 然后依次从样例数据库中读取图片出来 # 还调用了 Transform(object)函数, 完成图像的调整和随机翻转工作 dataloader = data_.DataLoader(dataset, \ batch_size=1, \ shuffle=True, \ # pin_memory=True, num_workers=opt.num_workers) testset = TestDataset(opt) test_dataloader = data_.DataLoader(testset, batch_size=1, num_workers=opt.test_num_workers, shuffle=False, \ pin_memory=True ) # 定义faster_rcnn=FasterRCNNVGG16 训练模型 faster_rcnn = FasterRCNNVGG16() print('model construct completed') # FasterRCNNVGG16 作为 fasterrcnn 的模型送入到 FasterRCNNTrainer 中并设置好GPU加速 trainer = FasterRCNNTrainer(faster_rcnn).cuda() if opt.load_path: trainer.load(opt.load_path) print('load pretrained model from %s' % opt.load_path) trainer.vis.text(dataset.db.label_names, win='labels') best_map = 0 lr_ = opt.lr for epoch in range(opt.epoch): trainer.reset_meters() for ii, (img, bbox_, label_, scale) in tqdm(enumerate(dataloader)): scale = at.scalar(scale) # 然后从训练数据中枚举dataloader, 设置好缩放范围, 将 img,bbox,label,scale 全部设置为可gpu加速 img, bbox, label = img.cuda().float(), bbox_.cuda(), label_.cuda() # 调用 trainer.py 中的函数 trainer.train_step(img,bbox,label,scale) 进行一次参数迭代优化过程 trainer.train_step(img, bbox, label, scale) if (ii + 1) % opt.plot_every == 0: if os.path.exists(opt.debug_file): ipdb.set_trace() # plot loss trainer.vis.plot_many(trainer.get_meter_data()) # plot groud truth bboxes ori_img_ = inverse_normalize(at.tonumpy(img[0])) gt_img = visdom_bbox(ori_img_, at.tonumpy(bbox_[0]), at.tonumpy(label_[0])) trainer.vis.img('gt_img', gt_img) # plot predicti bboxes # 调用 faster_rcnn 的 predict 进行预测, 预测的结果保留在以_下划线开头的对象里面 _bboxes, _labels, _scores = trainer.faster_rcnn.predict([ori_img_], visualize=True) pred_img = visdom_bbox(ori_img_, at.tonumpy(_bboxes[0]), at.tonumpy(_labels[0]).reshape(-1), at.tonumpy(_scores[0])) # 利用同样的方法将原始图片以及边框类别的预测结果 同样在可视化工具中显示出来 trainer.vis.img('pred_img', pred_img) # rpn confusion matrix(meter) # 调用 trainer.vis.text 将 rpn_cm 也就是 RPN网络的混淆矩阵在可视化工具中显示出来 trainer.vis.text(str(trainer.rpn_cm.value().tolist()), win='rpn_cm') # roi confusion matrix # 可视化 ROI_head 的混淆矩阵 trainer.vis.img('roi_cm', at.totensor(trainer.roi_cm.conf, False).float()) # 调用 eval 函数计算 map 等指标 eval_result = eval(test_dataloader, faster_rcnn, test_num=opt.test_num) # 可视化 map trainer.vis.plot('test_map', eval_result['map']) lr_ = trainer.faster_rcnn.optimizer.param_groups[0]['lr'] log_info = 'lr:{}, map:{},loss:{}'.format(str(lr_), str(eval_result['map']), str(trainer.get_meter_data())) # 将损失学习率以及map等信息及时显示更新 trainer.vis.log(log_info) # 用 if 判断语句永远保存效果最好的 map if eval_result['map'] > best_map: best_map = eval_result['map'] best_path = trainer.save(best_map=best_map) if epoch == 9: # if判断语句如果学习的epoch达到了9就将学习率*0.1: 变成原来的十分之一 trainer.load(best_path) trainer.faster_rcnn.scale_lr(opt.lr_decay) lr_ = lr_ * opt.lr_decay if epoch == 13: break ```这里我们看到, train.py仅是封装了一个 dataloader 函数, 以及 faster_rcnn 以及 FasterRCNNTrainer类. faster_rcnn是 faster_rcnn 的主体构件. FasterRCNNTrainer类封抽象了 faster_rcnn 算法的训练及预测步骤. 如图:

上图形象粗略地展示了大致的训练过程. 构造了 trainer 对象后, 紧接着通过 dataloader 对象获取数据, 进入 trainer.train_step(img, bbox, label, scale) 了. 那么我们赶紧进入最重要的类 FasterRCNNTrainer.
trainer.py
FasterRCNNTrainer 类在将整个架构图串起来了, 定义了四个损失函数, 将提取的特征 feature map、 RPN网络、ROI Pooling 以及 R-CNN网络 结合在了一起. 我们展开来看:
点击显示: trainer_py
```python class FasterRCNNTrainer(nn.Module): """wrapper for conveniently training. return losses The losses include: * :obj:`rpn_loc_loss`: The localization loss for \ Region Proposal Network (RPN). * :obj:`rpn_cls_loss`: The classification loss for RPN. * :obj:`roi_loc_loss`: The localization loss for the head module. * :obj:`roi_cls_loss`: The classification loss for the head module. * :obj:`total_loss`: The sum of 4 loss above. Args: faster_rcnn (model.FasterRCNN): A Faster R-CNN model that is going to be trained. """ def __init__(self, faster_rcnn): super(FasterRCNNTrainer, self).__init__() self.faster_rcnn = faster_rcnn # 下面两个参数是在 _faster_rcnn_loc_loss 调用用来计算位置损失函数用到的超参数 self.rpn_sigma = opt.rpn_sigma self.roi_sigma = opt.roi_sigma # target creator create gt_bbox gt_label etc as training targets. # 用于从20000个候选 anchor 中产生256个 anchor 进行二分类和位置回归 # 也就是为 rpn 网络产生的预测位置和预测类别提供 ground_truth 标准 self.anchor_target_creator = AnchorTargetCreator() # AnchorTargetCreator 和 ProposalTargetCreator 是为生成训练的目标(ground_truth)-仅在训练中使用 # ProposalCreator 是 RPN 为FasterRCNN生成 ROIs, 在训练与测试中都会用到. # 测试阶段直接输进来300个ROIs, 而训练阶段会有 AnchorTargetCreator 的再次干预 self.proposal_target_creator = ProposalTargetCreator() self.loc_normalize_mean = faster_rcnn.loc_normalize_mean self.loc_normalize_std = faster_rcnn.loc_normalize_std self.optimizer = self.faster_rcnn.get_optimizer() # visdom wrapper self.vis = Visualizer(env=opt.env) # indicators for training status # 混淆矩阵, 验证预测值与真实值精确度的矩阵 ConfusionMeter ()中未类别数 self.rpn_cm = ConfusionMeter(2) self.roi_cm = ConfusionMeter(21) # 平均损失 self.meters = {k: AverageValueMeter() for k in LossTuple._fields} # average loss # imgs: 图片; bboxes: 图片上所有 bbox 及 label def forward(self, imgs, bboxes, labels, scale): """Forward Faster R-CNN and calculate losses. Here are notations used. * :math:`N` is the batch size. * :math:`R` is the number of bounding boxes per image. Currently, only :math:`N=1` is supported. Args: imgs (~torch.autograd.Variable): A variable with a batch of images. bboxes (~torch.autograd.Variable): A batch of bounding boxes. Its shape is :math:`(N, R, 4)`. labels (~torch.autograd..Variable): A batch of labels. Its shape is :math:`(N, R)`. The background is excluded from the definition, which means that the range of the value is :math:`[0, L - 1]`. :math:`L` is the number of foreground classes. scale (float): Amount of scaling applied to the raw image during preprocessing. Returns: namedtuple of 5 losses """ n = bboxes.shape[0] if n != 1: raise ValueError('Currently only batch size 1 is supported.') _, _, H, W = imgs.shape # n, c, h, w img_size = (H, W) # vgg16 conv5_3 之前的部分提取图片的特征 features = self.faster_rcnn.extractor(imgs) # rpn_locs 的维度(hh*ww*9, 4), rpn_scores 维度为 (hh*ww*9, 2) # rois维度为 (2000, 4), roi_indices用不到, anchor维度为(hh*ww*9, 4)约20 000个 # H,W 是经过数据预处理后的. # 计算(H/16)*(W/16)*9(大概20 000个) anchor属于前景的概率取前 12000 个并经过 NMS 得到 2000个近似目标框G^的坐标(后面处理用的). rpn_locs, rpn_scores, rois, roi_indices, anchor = \ self.faster_rcnn.rpn(features, img_size, scale) # Since batch size is one, convert variables to singular form bbox = bboxes[0] # (N, R, 4) label = labels[0] # (N, R) rpn_score = rpn_scores[0] # (hh*ww*9) rpn_loc = rpn_locs[0] # (hh*ww*9) roi = rois # (2000, 4) # Sample RoIs and forward # it's fine to break the computation graph of rois, # consider them as constant input # 调用 proposal_target_creator 生成 sample_roi(128, 4), gt_roi_loc(128, 4), gt_roi_label(128, 1) # ROIHead 网络利用 sample_roi + feature 为输入, 输出是分类(21)和回归(微调bbox)的预测值 # 那么回归分类的 groud_truth 就是 ProposalTargetCreator 输出的 gt_roi_label, gt_roi_loc sample_roi, gt_roi_loc, gt_roi_label = self.proposal_target_creator( roi, at.tonumpy(bbox), at.tonumpy(label), self.loc_normalize_mean, self.loc_normalize_std) # NOTE it's all zero because now it only support for batch=1 now sample_roi_index = t.zeros(len(sample_roi)) # roi 回归输出 128*84 和 128*21, 然而真实位置参数是 128*4, 真实标签是 128*1 roi_cls_loc, roi_score = self.faster_rcnn.head( features, sample_roi, sample_roi_index) # ------------------ RPN losses -------------------# # 输入 20000个 anchor 和 bbox, 调用 anchor_target_creator 函数得到2000 个anchor与bbox的偏移量与label gt_rpn_loc, gt_rpn_label = self.anchor_target_creator( at.tonumpy(bbox), anchor, img_size) gt_rpn_label = at.totensor(gt_rpn_label).long() gt_rpn_loc = at.totensor(gt_rpn_loc) # rpn_loc 为 rpn网络回归出来的偏移量(20000) # gt_rpn_loc 为 anchor_target_creator 函数得到2000个anchor 与 bbox 的偏移量 rpn_sigma=1 rpn_loc_loss = _fast_rcnn_loc_loss( rpn_loc, gt_rpn_loc, gt_rpn_label.data, self.rpn_sigma) # NOTE: default value of ignore_index is -100 # rpn_score 为 rpn 网络得到的(20000) 与 anchor_target_creator 得到的2000个label求交叉熵损失 rpn_cls_loss = F.cross_entropy(rpn_score, gt_rpn_label.cuda(), ignore_index=-1) _gt_rpn_label = gt_rpn_label[gt_rpn_label > -1] # 不计算背景类 _rpn_score = at.tonumpy(rpn_score)[at.tonumpy(gt_rpn_label) > -1] self.rpn_cm.add(at.totensor(_rpn_score, False), _gt_rpn_label.data.long()) # ------------------ ROI losses (fast rcnn loss) -------------------# # roi_cls_loc 为 VGG16RoIHead 的输出 (128*84), n_sample=128 n_sample = roi_cls_loc.shape[0] # roi_cls_loc: (128, 21, 4) roi_cls_loc = roi_cls_loc.view(n_sample, -1, 4) roi_loc = roi_cls_loc[t.arange(0, n_sample).long().cuda(), \ at.totensor(gt_roi_label).long()] # proposal_target_creator 生成的128个 proposal 与 bbox 求得的偏移量 # dx, dy, dw, dh gt_roi_label = at.totensor(gt_roi_label).long() # 128个标签 gt_roi_loc = at.totensor(gt_roi_loc) # smooth_l1_loss roi_loc_loss = _fast_rcnn_loc_loss( roi_loc.contiguous(), gt_roi_loc, gt_roi_label.data, self.roi_sigma) roi_cls_loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()(roi_score, gt_roi_label.cuda()) self.roi_cm.add(at.totensor(roi_score, False), gt_roi_label.data.long()) losses = [rpn_loc_loss, rpn_cls_loss, roi_loc_loss, roi_cls_loss] losses = losses + [sum(losses)] return LossTuple(*losses) def train_step(self, imgs, bboxes, labels, scale): self.optimizer.zero_grad() losses = self.forward(imgs, bboxes, labels, scale) losses.total_loss.backward() self.optimizer.step() self.update_meters(losses) return losses ```是不是发现 train_step 很简单?前向, 后向计算loss, 更新参数这几步. 主要的是在 forward 上.

我们先看 __init__ 部分, 传入了 fasterRCNNVGG16 的实例化对象 faster_rcnn ;
AnchorTargetCreator为 rpn网络 提供预测位置与类别的 ground_truth 标准, 它将约20 000 个 anchor 进行筛选(我们上面介绍的, 根据与object的重合程度来判定正负样本), 得到256个 anchor;
ProposalTargetCreator 将 rpn网络生成的大量 rois 进行筛选, 得到128个 sample_rois 送入接下来的 ROI Pooling 部分.
我们重点介绍forward 部分. 从 dataloader 获得 imgs、 bboxes labels . 结合架构图, 我们知道首先使用骨干网络 vgg 提取到 features,
然后送入 rpn 网络中提取得到 roi 区域, 然后通过 ProposalTargetCreator 对 rois 进行筛选 (如何筛选详见后面) , 得到128个的 sample_roi 送入 ROI Pooling 中后再送入 R-CNN 得到最后的分类与回归结果, 这两个部分都在 faster_rcnn.head 中.
FasterRCNN
既然 faster_rcnn 类包含了整个算法的核心部件. 如下图所示, 最重要的就是 vgg提特征、 RPN、 R-CNN三个部分(ROI pooling 算R-CNN部分).

这里将三个部分最终要的部分组合进入 FasterRCNNVGG16 中。
点击显示: faster_rcnn_vgg16.py
```python # 分别对 VGG16 的特征提取部分, 分类部分, RPN网络, VGG16RoIHead 网络进行实例化 class FasterRCNNVGG16(FasterRCNN): """Faster R-CNN based on VGG-16. For descriptions on the interface of this model, please refer to :class:`model.faster_rcnn.FasterRCNN`. Args: n_fg_class (int): The number of classes excluding the background. ratios (list of floats): This is ratios of width to height of the anchors. anchor_scales (list of numbers): This is areas of anchors. Those areas will be the product of the square of an element in :obj:`anchor_scales` and the original area of the reference window. """ # vgg16 通过5个stage 下采样16倍 feat_stride = 16 # downsample 16x for output of conv5 in vgg16 # 总类别数为20类, 三种尺度三种比例的 anchor def __init__(self, n_fg_class=20, ratios=[0.5, 1, 2], anchor_scales=[8, 16, 32] ): # conv5_3 及之前的特征提取部分, 分类器 extractor, classifier = decom_vgg16() # 返回 rpn_locs, rpn_scores, rois, roi_indices, anchor rpn = RegionProposalNetwork( 512, 512, ratios=ratios, anchor_scales=anchor_scales, feat_stride=self.feat_stride, ) head = VGG16RoIHead( n_class=n_fg_class + 1, roi_size=7, spatial_scale=(1. / self.feat_stride), classifier=classifier ) super(FasterRCNNVGG16, self).__init__( extractor, rpn, head, ) ```代码不难理解. 类继承自 FasterRCNN , forward 在父类中实现了:
点击显示: faster_rcnn.py
```python class FasterRCNN(nn.Module): """Base class for Faster R-CNN. This is a base class for Faster R-CNN links supporting object detection API [#]_. The following three stages constitute Faster R-CNN. 1. **Feature extraction**: Images are taken and their \ feature maps are calculated. 2. **Region Proposal Networks**: Given the feature maps calculated in \ the previous stage, produce set of RoIs around objects. 3. **Localization and Classification Heads**: Using feature maps that \ belong to the proposed RoIs, classify the categories of the objects \ in the RoIs and improve localizations. Each stage is carried out by one of the callable :class:`torch.nn.Module` objects :obj:`feature`, :obj:`rpn` and :obj:`head`. There are two functions :meth:`predict` and :meth:`__call__` to conduct object detection. :meth:`predict` takes images and returns bounding boxes that are converted to image coordinates. This will be useful for a scenario when Faster R-CNN is treated as a black box function, for instance. :meth:`__call__` is provided for a scnerario when intermediate outputs are needed, for instance, for training and debugging. Links that support obejct detection API have method :meth:`predict` with the same interface. Please refer to :meth:`predict` for further details. .. [#] Shaoqing Ren, Kaiming He, Ross Girshick, Jian Sun. \ Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with \ Region Proposal Networks. NIPS 2015. Args: extractor (nn.Module): A module that takes a BCHW image array and returns feature maps. rpn (nn.Module): A module that has the same interface as :class:`model.region_proposal_network.RegionProposalNetwork`. Please refer to the documentation found there. head (nn.Module): A module that takes a BCHW variable, RoIs and batch indices for RoIs. This returns class dependent localization paramters and class scores. loc_normalize_mean (tuple of four floats): Mean values of localization estimates. loc_normalize_std (tupler of four floats): Standard deviation of localization estimates. """ def __init__(self, extractor, rpn, head, loc_normalize_mean = (0., 0., 0., 0.), loc_normalize_std = (0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2) ): super(FasterRCNN, self).__init__() self.extractor = extractor self.rpn = rpn self.head = head # mean and std self.loc_normalize_mean = loc_normalize_mean self.loc_normalize_std = loc_normalize_std self.use_preset('evaluate') @property def n_class(self): # Total number of classes including the background. return self.head.n_class def forward(self, x, scale=1.): """Forward Faster R-CNN. Scaling paramter :obj:`scale` is used by RPN to determine the threshold to select small objects, which are going to be rejected irrespective of their confidence scores. Here are notations used. * :math:`N` is the number of batch size * :math:`R'` is the total number of RoIs produced across batches. \ Given :math:`R_i` proposed RoIs from the :math:`i` th image, \ :math:`R' = \\sum _{i=1} ^ N R_i`. * :math:`L` is the number of classes excluding the background. Classes are ordered by the background, the first class, ..., and the :math:`L` th class. Args: x (autograd.Variable): 4D image variable. scale (float): Amount of scaling applied to the raw image during preprocessing. Returns: Variable, Variable, array, array: Returns tuple of four values listed below. * **roi_cls_locs**: Offsets and scalings for the proposed RoIs. \ Its shape is :math:`(R', (L + 1) \\times 4)`. * **roi_scores**: Class predictions for the proposed RoIs. \ Its shape is :math:`(R', L + 1)`. * **rois**: RoIs proposed by RPN. Its shape is \ :math:`(R', 4)`. * **roi_indices**: Batch indices of RoIs. Its shape is \ :math:`(R',)`. """ img_size = x.shape[2:] h = self.extractor(x) rpn_locs, rpn_scores, rois, roi_indices, anchor = \ self.rpn(h, img_size, scale) roi_cls_locs, roi_scores = self.head( h, rois, roi_indices) return roi_cls_locs, roi_scores, rois, roi_indices ```怎么回事? rpn 和 head 还没有看到? 是的. 不急, 我们还需要继续深入.

RPN网络

点击显示: region_proposal_network.py
```python class RegionProposalNetwork(nn.Module): """Region Proposal Network introduced in Faster R-CNN. This is Region Proposal Network introduced in Faster R-CNN [#]_. This takes features extracted from images and propose class agnostic bounding boxes around "objects". .. [#] Shaoqing Ren, Kaiming He, Ross Girshick, Jian Sun. \ Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with \ Region Proposal Networks. NIPS 2015. Args: in_channels (int): The channel size of input. mid_channels (int): The channel size of the intermediate tensor. ratios (list of floats): This is ratios of width to height of the anchors. anchor_scales (list of numbers): This is areas of anchors. Those areas will be the product of the square of an element in :obj:`anchor_scales` and the original area of the reference window. feat_stride (int): Stride size after extracting features from an image. initialW (callable): Initial weight value. If :obj:`None` then this function uses Gaussian distribution scaled by 0.1 to initialize weight. May also be a callable that takes an array and edits its values. proposal_creator_params (dict): Key valued paramters for :class:`model.utils.creator_tools.ProposalCreator`. .. see also:: :class:`~model.utils.creator_tools.ProposalCreator` """ def __init__( self, in_channels=512, mid_channels=512, ratios=[0.5, 1, 2], anchor_scales=[8, 16, 32], feat_stride=16, proposal_creator_params=dict(), ): super(RegionProposalNetwork, self).__init__() # 首先生成上述以 (0,0) 为中心的9个base anchor self.anchor_base = generate_anchor_base( anchor_scales=anchor_scales, ratios=ratios) self.feat_stride = feat_stride self.proposal_layer = ProposalCreator(self, **proposal_creator_params) n_anchor = self.anchor_base.shape[0] # nn.Conv2d in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, padding self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, mid_channels, 3, 1, 1) self.score = nn.Conv2d(mid_channels, n_anchor * 2, 1, 1, 0) self.loc = nn.Conv2d(mid_channels, n_anchor * 4, 1, 1, 0) normal_init(self.conv1, 0, 0.01) normal_init(self.score, 0, 0.01) normal_init(self.loc, 0, 0.01) def forward(self, x, img_size, scale=1.): """Forward Region Proposal Network. Here are notations. * :math:`N` is batch size. * :math:`C` channel size of the input. * :math:`H` and :math:`W` are height and witdh of the input feature. * :math:`A` is number of anchors assigned to each pixel. Args: x (~torch.autograd.Variable): The Features extracted from images. Its shape is :math:`(N, C, H, W)`. img_size (tuple of ints): A tuple :obj:`height, width`, which contains image size after scaling. scale (float): The amount of scaling done to the input images after reading them from files. Returns: (~torch.autograd.Variable, ~torch.autograd.Variable, array, array, array): This is a tuple of five following values. * **rpn_locs**: Predicted bounding box offsets and scales for \ anchors. Its shape is :math:`(N, H W A, 4)`. * **rpn_scores**: Predicted foreground scores for \ anchors. Its shape is :math:`(N, H W A, 2)`. * **rois**: A bounding box array containing coordinates of \ proposal boxes. This is a concatenation of bounding box \ arrays from multiple images in the batch. \ Its shape is :math:`(R', 4)`. Given :math:`R_i` predicted \ bounding boxes from the :math:`i` th image, \ :math:`R' = \\sum _{i=1} ^ N R_i`. * **roi_indices**: An array containing indices of images to \ which RoIs correspond to. Its shape is :math:`(R',)`. * **anchor**: Coordinates of enumerated shifted anchors. \ Its shape is :math:`(H W A, 4)`. """ # x的尺寸为(batch_size, 512, H/16, W/16), 其中H,W分别为原图的高和宽 # x为feature map, n为batch_size, 此版本代码为1. hh, ww即为宽高 n, _, hh, ww = x.shape # 在9个 base_anchor 基础上生成 hh*ww*9个 anchor, 对应到原图坐标 feat_stride=16 # 因为是经4次pool后提到的特征, 故feature map较原图缩小了16倍 anchor = _enumerate_shifted_anchor( np.array(self.anchor_base), self.feat_stride, hh, ww) # (hh * ww * 9) / hh*ww = 9 n_anchor = anchor.shape[0] // (hh * ww) # 512 个 3x3 卷积 (512, H/16, W/16) h = F.relu(self.conv1(x)) # n_anchor (9)*4 个1x1卷积, 回归坐标偏移量 (9*4,hh,ww) rpn_locs = self.loc(h) # UNNOTE: check whether need contiguous # A: Yes # 转换为 (n,hh,ww,9*4) 后变为 (n,hh*ww*9,4) rpn_locs = rpn_locs.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous().view(n, -1, 4) # n_anchor (9)*2个1x1卷积, 回归类别 (9*2,hh,ww) rpn_scores = self.score(h) # 转换为 (n, hh, ww, 9*2) rpn_scores = rpn_scores.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous() # 计算{Softmax}(x_{i}) = \{exp(x_i)}{\sum_j exp(x_j)} rpn_softmax_scores = F.softmax(rpn_scores.view(n, hh, ww, n_anchor, 2), dim=4) # 得到前景的分类概率 rpn_fg_scores:(n,hh,ww,n_anchor, 1) rpn_fg_scores = rpn_softmax_scores[:, :, :, :, 1].contiguous() # 得到所有 anchor 的前景分类概率 (n, hh*ww*n_anchor) rpn_fg_scores = rpn_fg_scores.view(n, -1) # 得到每一张 feature map 上所有 anchor 的网络输出值 (n, hh*ww*9, 2) rpn_scores = rpn_scores.view(n, -1, 2) rois = list() roi_indices = list() # n为batch_size数 rpn_locs: (n,hh*ww*9,4) rpn_fg_scores: (n, hh*ww*n_anchor) for i in range(n): # 调用 ProposalCreator 函数, rpn_locs 维度(hh*ww*9,4) # rpn_fg_scores 维度为(hh*ww*9), anchor的维度为(hh*ww*9, 4) # img_size 的维度为 (3,H,W) H和W是经过数据预处理后的 # 计算 (H/16)x(W/16)x9 (大概20000)个anchor属于前景的概率, # 取前12000个并经过NMS得到2000个近似目标框G^的坐标。roi的维度为(2000,4) roi = self.proposal_layer( rpn_locs[i].cpu().data.numpy(), rpn_fg_scores[i].cpu().data.numpy(), anchor, img_size, scale=scale) batch_index = i * np.ones((len(roi),), dtype=np.int32) # rois 为所有 batch_size 的 roi rois.append(roi) roi_indices.append(batch_index) # 按行拼接(即没有batch_size的区分, 每一个[]里都是一个anchor的四个坐标) rois = np.concatenate(rois, axis=0) # 这个 roi_indices 在此代码中是多余的, 因为我们实现的是 batch_size=1 的网络 # 一个batch只会输入一张图象. 如果多张图像的话就需要存储索引以找到对应图像的roi roi_indices = np.concatenate(roi_indices, axis=0) # rpn_locs 的维度 (hh*ww*9, 4) rpn_scores 维度为 (hh*ww*9, 2) # rois 的维度为(2000,4) roi_indices 用不到 anchor 的维度为 (hh*ww*9, 4) return rpn_locs, rpn_scores, rois, roi_indices, anchor ```数据进入 forward 中, 获取维度. 之后得到 hh*ww*9 个 anchor . 对数据进行 3x3 卷积, 之后是 loc 和 score 卷积, 分别得到分类结果与回归结果. 对 rpn_scores 进行 softmax 得到前景概率, 将前景概率送入 self.proposal_layer (经 NMS 得到粗 roi 区域, 之后详解 ProposalCreator).
R-CNN
再次回到 faster_rcnn_vgg16.VGG16RoIHead 部分, 这里包含了 ROI Pooling 和 R-CNN分类与回归两部分.
点击显示: VGG16RoIHead.py
```python class VGG16RoIHead(nn.Module): """Faster R-CNN Head for VGG-16 based implementation. This class is used as a head for Faster R-CNN. This outputs class-wise localizations and classification based on feature maps in the given RoIs. Args: n_class (int): The number of classes possibly including the background. roi_size (int): Height and width of the feature maps after RoI-pooling. spatial_scale (float): Scale of the roi is resized. classifier (nn.Module): Two layer Linear ported from vgg16 """ def __init__(self, n_class, roi_size, spatial_scale, classifier): # n_class includes the background super(VGG16RoIHead, self).__init__() # vgg16 中最后两个全连接层 self.classifier = classifier self.cls_loc = nn.Linear(4096, n_class * 4) self.score = nn.Linear(4096, n_class) # 全连接层权重初始化 normal_init(self.cls_loc, 0, 0.001) normal_init(self.score, 0, 0.01) # 加上背景一共21类 self.n_class = n_class self.roi_size = roi_size # 7x7 self.spatial_scale = spatial_scale # 1/16 # 将大小不同的 roi 变成大小一致, 得到 pooling 后的特征大小为[300, 512, 7, 7] self.roi = RoIPool( (self.roi_size, self.roi_size), self.spatial_scale) def forward(self, x, rois, roi_indices): """Forward the chain. We assume that there are :math:`N` batches. Args: x (Variable): 4D image variable. rois (Tensor): A bounding box array containing coordinates of proposal boxes. This is a concatenation of bounding box arrays from multiple images in the batch. Its shape is :math:`(R', 4)`. Given :math:`R_i` proposed RoIs from the :math:`i` th image, :math:`R' = \\sum _{i=1} ^ N R_i`. roi_indices (Tensor): An array containing indices of images to which bounding boxes correspond to. Its shape is :math:`(R',)`. """ # 前面解释过这里的 roi_indices 其实是多余的, 因为 batch_size 一直为1 # in case roi_indices is ndarray roi_indices = at.totensor(roi_indices).float() rois = at.totensor(rois).float() indices_and_rois = t.cat([roi_indices[:, None], rois], dim=1) # NOTE: important: yx->xy xy_indices_and_rois = indices_and_rois[:, [0, 2, 1, 4, 3]] # 把 tensor 变成在内存中连续分布的形式 indices_and_rois = xy_indices_and_rois.contiguous() # 接下来分析 roi_module.py 中的 RoI() pool = self.roi(x, indices_and_rois) # flat操作 pool = pool.view(pool.size(0), -1) # decom_vgg16()得到的calssifier,得到4096 fc7 = self.classifier(pool) # (4096->84) roi_cls_locs = self.cls_loc(fc7) # (4096->21) roi_scores = self.score(fc7) return roi_cls_locs, roi_scores ```这一部分基本没什么难点, 基本就是 RoIPool 与多个全连接分类与回归。结合流程图理解吧.

接下来就是基础工具 ProposalCreator 、 ProposalTargetCreator 与 AnchorTargetCreator 了.
ProposalCreator & ProposalTargetCreator & AnchorTargetCreator

点击显示: creator_tool.py
```python # ProposalCreator 产生 2000 个 ROIs, 但是这些 ROIs 并不都用于训练 # 经本函数筛选产生128个用于自身训练 class ProposalTargetCreator(object): """Assign ground truth bounding boxes to given RoIs. The :meth:`__call__` of this class generates training targets for each object proposal. This is used to train Faster RCNN [#]_. .. [#] Shaoqing Ren, Kaiming He, Ross Girshick, Jian Sun. \ Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with \ Region Proposal Networks. NIPS 2015. Args: n_sample (int): The number of sampled regions. pos_ratio (float): Fraction of regions that is labeled as a foreground. pos_iou_thresh (float): IoU threshold for a RoI to be considered as a foreground. neg_iou_thresh_hi (float): RoI is considered to be the background if IoU is in [:obj:`neg_iou_thresh_hi`, :obj:`neg_iou_thresh_hi`). neg_iou_thresh_lo (float): See above. """ def __init__(self, n_sample=128, pos_ratio=0.25, pos_iou_thresh=0.5, neg_iou_thresh_hi=0.5, neg_iou_thresh_lo=0.0 ): self.n_sample = n_sample self.pos_ratio = pos_ratio self.pos_iou_thresh = pos_iou_thresh self.neg_iou_thresh_hi = neg_iou_thresh_hi self.neg_iou_thresh_lo = neg_iou_thresh_lo # NOTE:default 0.1 in py-faster-rcnn # 输入: 2000个rois, 一个batch(一张图) 中所有的bbox ground truth(R, 4), # 对应bbox所包含的label(R, 1) (VOC2007来说20类0-19) # 输出: 128个sample roi(128,4), 128个gt_roi_loc(128, 4), # 128个gt_roi_label(128, 1) def __call__(self, roi, bbox, label, loc_normalize_mean=(0., 0., 0., 0.), loc_normalize_std=(0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2)): """Assigns ground truth to sampled proposals. This function samples total of :obj:`self.n_sample` RoIs from the combination of :obj:`roi` and :obj:`bbox`. The RoIs are assigned with the ground truth class labels as well as bounding box offsets and scales to match the ground truth bounding boxes. As many as :obj:`pos_ratio * self.n_sample` RoIs are sampled as foregrounds. Offsets and scales of bounding boxes are calculated using :func:`model.utils.bbox_tools.bbox2loc`. Also, types of input arrays and output arrays are same. Here are notations. * :math:`S` is the total number of sampled RoIs, which equals \ :obj:`self.n_sample`. * :math:`L` is number of object classes possibly including the \ background. Args: roi (array): Region of Interests (RoIs) from which we sample. Its shape is :math:`(R, 4)` bbox (array): The coordinates of ground truth bounding boxes. Its shape is :math:`(R', 4)`. label (array): Ground truth bounding box labels. Its shape is :math:`(R',)`. Its range is :math:`[0, L - 1]`, where :math:`L` is the number of foreground classes. loc_normalize_mean (tuple of four floats): Mean values to normalize coordinates of bouding boxes. loc_normalize_std (tupler of four floats): Standard deviation of the coordinates of bounding boxes. Returns: (array, array, array): * **sample_roi**: Regions of interests that are sampled. \ Its shape is :math:`(S, 4)`. * **gt_roi_loc**: Offsets and scales to match \ the sampled RoIs to the ground truth bounding boxes. \ Its shape is :math:`(S, 4)`. * **gt_roi_label**: Labels assigned to sampled RoIs. Its shape is \ :math:`(S,)`. Its range is :math:`[0, L]`. The label with \ value 0 is the background. """ n_bbox, _ = bbox.shape # 首先将2000个roi和m个bbox给concatenate了一下成为新的roi (2000+m, 4). roi = np.concatenate((roi, bbox), axis=0) # n_sample=128, pos_ratio=0.5, round 对传入的数据进行四舍五入 pos_roi_per_image = np.round(self.n_sample * self.pos_ratio) # 计算每一个roi与每一个bbox的iou shape: (2000+m, m) iou = bbox_iou(roi, bbox) # 按行找到最大值, 返回最大值对应的序号以及其真正的IOU # 返回的是每个roi与哪个bbox的最大, 以及最大的iou值 gt_assignment = iou.argmax(axis=1) # 每个roi与对应bbox最大的iou max_iou = iou.max(axis=1) # Offset range of classes from [0, n_fg_class - 1] to [1, n_fg_class]. # The label with value 0 is the background. # 从1开始的类别序号, 给每个类得到真正的label(将0-19变为1-20) gt_roi_label = label[gt_assignment] + 1 # Select foreground RoIs as those with >= pos_iou_thresh IoU. # 根据iou的最大值将正负样本找出来, pos_iou_thresh=0.5 pos_index = np.where(max_iou >= self.pos_iou_thresh)[0] # 需要保留的roi个数(满足大于pos_iou_thresh条件的roi与64之间较小的一个) pos_roi_per_this_image = int(min(pos_roi_per_image, pos_index.size)) if pos_index.size > 0: pos_index = np.random.choice( pos_index, size=pos_roi_per_this_image, replace=False) # Select background RoIs as those within # [neg_iou_thresh_lo, neg_iou_thresh_hi). # neg_iou_thresh_hi=0.5, neg_iou_thresh_lo=0.0 neg_index = np.where((max_iou < self.neg_iou_thresh_hi) & (max_iou >= self.neg_iou_thresh_lo))[0] neg_roi_per_this_image = self.n_sample - pos_roi_per_this_image neg_roi_per_this_image = int(min(neg_roi_per_this_image, neg_index.size)) if neg_index.size > 0: neg_index = np.random.choice( neg_index, size=neg_roi_per_this_image, replace=False) # The indices that we're selecting (both positive and negative). keep_index = np.append(pos_index, neg_index) gt_roi_label = gt_roi_label[keep_index] # 每个ROI的label gt_roi_label[pos_roi_per_this_image:] = 0 # negative labels --> 0 sample_roi = roi[keep_index] # 此时输出的128*4的 sample_roi 就可以去扔到 RoIHead 网络里去进行分类与回归了. # 同样, RoIHead 网络利用这sample_roi+featue为输入, 输出 # 是分类(21类)和回归(进一步微调bbox)的预测值, 那么分类回归的 groud truth # 就是 ProposalTargetCreator 输出的 gt_roi_label 和 gt_roi_loc. # 求这128个样本的 groundtruth # Compute offsets and scales to match sampled RoIs to the GTs. gt_roi_loc = bbox2loc(sample_roi, bbox[gt_assignment[keep_index]]) # ProposalTargetCreator首次用到了真实的21个类的label, # 且该类最后对 loc 进行了归一化处理, 所以预测时要进行均值方差处理 gt_roi_loc = ((gt_roi_loc - np.array(loc_normalize_mean, np.float32) ) / np.array(loc_normalize_std, np.float32)) return sample_roi, gt_roi_loc, gt_roi_label # 将20000多个候选的 Anchor 选出 生成训练要用的anchor(正负样本各128个框的坐标和256个label) class AnchorTargetCreator(object): """Assign the ground truth bounding boxes to anchors. Assigns the ground truth bounding boxes to anchors for training Region Proposal Networks introduced in Faster R-CNN [#]_. Offsets and scales to match anchors to the ground truth are calculated using the encoding scheme of :func:`model.utils.bbox_tools.bbox2loc`. .. [#] Shaoqing Ren, Kaiming He, Ross Girshick, Jian Sun. \ Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with \ Region Proposal Networks. NIPS 2015. Args: n_sample (int): The number of regions to produce. pos_iou_thresh (float): Anchors with IoU above this threshold will be assigned as positive. neg_iou_thresh (float): Anchors with IoU below this threshold will be assigned as negative. pos_ratio (float): Ratio of positive regions in the sampled regions. """ def __init__(self, n_sample=256, pos_iou_thresh=0.7, neg_iou_thresh=0.3, pos_ratio=0.5): self.n_sample = n_sample self.pos_iou_thresh = pos_iou_thresh self.neg_iou_thresh = neg_iou_thresh self.pos_ratio = pos_ratio def __call__(self, bbox, anchor, img_size): """Assign ground truth supervision to sampled subset of anchors. Types of input arrays and output arrays are same. Here are notations. * :math:`S` is the number of anchors. * :math:`R` is the number of bounding boxes. Args: bbox (array): Coordinates of bounding boxes. Its shape is :math:`(R, 4)`. anchor (array): Coordinates of anchors. Its shape is :math:`(S, 4)`. img_size (tuple of ints): A tuple :obj:`H, W`, which is a tuple of height and width of an image. Returns: (array, array): #NOTE: it's scale not only offset * **loc**: Offsets and scales to match the anchors to \ the ground truth bounding boxes. Its shape is :math:`(S, 4)`. * **label**: Labels of anchors with values \ :obj:`(1=positive, 0=negative, -1=ignore)`. Its shape \ is :math:`(S,)`. """ # 特征图大小 img_H, img_W = img_size # 一般对应 20000 个左右 anchor n_anchor = len(anchor) # 将超出图片范围的 anchor 全部去掉, 只保留图片内部的的序号 inside_index = _get_inside_index(anchor, img_H, img_W) # 保留位于图片内部的 anchor anchor = anchor[inside_index] # 筛选出符合条件的正例128个 负例128个-->以及他们的label; ?:argmax_ious (S, ); label: (256, ) argmax_ious, label = self._create_label( inside_index, anchor, bbox) # compute bounding box regression targets # 计算每一个anchor与对应bbox求得iou最大的 bbox 计算偏移量(这里是每一个) shape: [20000, 4] loc = bbox2loc(anchor, bbox[argmax_ious]) # map up to original set of anchors # 将位于图片内部的框的label对应到所有生成的20000个框中 (label原本为所有在图片中的框) label = _unmap(label, n_anchor, inside_index, fill=-1) # 将回归的框对应到所有生成的20000个框中(label原本为所有在图片中的框的) loc = _unmap(loc, n_anchor, inside_index, fill=0) return loc, label def _create_label(self, inside_index, anchor, bbox): # inside_index为所有在图片范围内的anchor序号 # label: 1 is positive, 0 is negative, -1 dont care label = np.empty((len(inside_index),), dtype=np.int32) label.fill(-1) # 调用_calc_ious() 函数得到每个anchor与哪个bbox的iou最大以及这个iou值、 # 每个bbox与哪个anchor的iou最大(需要体会从行和列取最大值的区别) argmax_ious, max_ious, gt_argmax_ious = \ self._calc_ious(anchor, bbox, inside_index) # assign negative labels first so that positive labels can clobber them # 把每个anchor与对应的框求得的iou值与负样本阈值比较, 若小于负样本阈值, 则label设为0 # pos_iou_thresh=0.7, neg_iou_thresh=0.3 label[max_ious < self.neg_iou_thresh] = 0 # positive label: for each gt, anchor with highest iou # 把与每个bbox求得iou值最大的anchor的label设为1 label[gt_argmax_ious] = 1 # positive label: above threshold IOU # 把每个anchor与对应的框求得的iou值与正样本阈值比较, 若大于正样本阈值, 则label设为1 label[max_ious >= self.pos_iou_thresh] = 1 # subsample positive labels if we have too many n_pos = int(self.pos_ratio * self.n_sample) pos_index = np.where(label == 1)[0] if len(pos_index) > n_pos: disable_index = np.random.choice( pos_index, size=(len(pos_index) - n_pos), replace=False) label[disable_index] = -1 # subsample negative labels if we have too many n_neg = self.n_sample - np.sum(label == 1) neg_index = np.where(label == 0)[0] if len(neg_index) > n_neg: disable_index = np.random.choice( neg_index, size=(len(neg_index) - n_neg), replace=False) label[disable_index] = -1 return argmax_ious, label # 每个 anchor 与哪个 bbox 的 iou 最大以及这个 iou 值; 每个 bbox 与哪个 anchor 的 iou 最大 def _calc_ious(self, anchor, bbox, inside_index): # ious between the anchors and the gt boxes # 调用 bbox_iou 函数计算 anchor 与 bbox 的 IOU, ious:(N,K) ious = bbox_iou(anchor, bbox) argmax_ious = ious.argmax(axis=1) # N anchor数 # 求出每个anchor与哪个bbox的iou最大, 以及最大值, max_ious:[1,N] max_ious = ious[np.arange(len(inside_index)), argmax_ious] gt_argmax_ious = ious.argmax(axis=0) # 求出每个bbox与哪个anchor的iou最大, 以及最大值,gt_max_ious:[1,K] gt_max_ious = ious[gt_argmax_ious, np.arange(ious.shape[1])] # 然后返回最大iou的索引(每个bbox与哪个anchor的iou最大), 有K个 gt_argmax_ious = np.where(ious == gt_max_ious)[0] return argmax_ious, max_ious, gt_argmax_ious # 提供ROIs给 ROI_head 作为训练样本: 选取概率较大的12000个Anchor # 利用回归的位置修正12000个Anchor, 获得ROIs; 非极大值抑制获得2000个ROIs class ProposalCreator: # unNOTE: I'll make it undifferential # unTODO: make sure it's ok # It's ok """Proposal regions are generated by calling this object. The :meth:`__call__` of this object outputs object detection proposals by applying estimated bounding box offsets to a set of anchors. This class takes parameters to control number of bounding boxes to pass to NMS and keep after NMS. If the paramters are negative, it uses all the bounding boxes supplied or keep all the bounding boxes returned by NMS. This class is used for Region Proposal Networks introduced in Faster R-CNN [#]_. .. [#] Shaoqing Ren, Kaiming He, Ross Girshick, Jian Sun. \ Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with \ Region Proposal Networks. NIPS 2015. Args: nms_thresh (float): Threshold value used when calling NMS. n_train_pre_nms (int): Number of top scored bounding boxes to keep before passing to NMS in train mode. n_train_post_nms (int): Number of top scored bounding boxes to keep after passing to NMS in train mode. n_test_pre_nms (int): Number of top scored bounding boxes to keep before passing to NMS in test mode. n_test_post_nms (int): Number of top scored bounding boxes to keep after passing to NMS in test mode. force_cpu_nms (bool): If this is :obj:`True`, always use NMS in CPU mode. If :obj:`False`, the NMS mode is selected based on the type of inputs. min_size (int): A paramter to determine the threshold on discarding bounding boxes based on their sizes. """ # 对于每张图片, 利用它的feature map, 计算(H/16)x(W/16)x9(大概20000)个 # anchor属于前景的概率, 然后从中选取概率较大的12000张, 利用位置回归参数, # 修正这12000个 anchor 的位置, 利用非极大值抑制选出2000个ROIs以及对应的位置参数 def __init__(self, parent_model, nms_thresh=0.7, n_train_pre_nms=12000, n_train_post_nms=2000, n_test_pre_nms=6000, n_test_post_nms=300, min_size=16 ): self.parent_model = parent_model self.nms_thresh = nms_thresh self.n_train_pre_nms = n_train_pre_nms self.n_train_post_nms = n_train_post_nms self.n_test_pre_nms = n_test_pre_nms self.n_test_post_nms = n_test_post_nms self.min_size = min_size # 这里的 loc 和 score 是经过 region_proposal_network 中经过1x1卷积分类和回归得到的 def __call__(self, loc, score, anchor, img_size, scale=1.): """input should be ndarray Propose RoIs. Inputs :obj:`loc, score, anchor` refer to the same anchor when indexed by the same index. On notations, :math:`R` is the total number of anchors. This is equal to product of the height and the width of an image and the number of anchor bases per pixel. Type of the output is same as the inputs. Args: loc (array): Predicted offsets and scaling to anchors. Its shape is :math:`(R, 4)`. score (array): Predicted foreground probability for anchors. Its shape is :math:`(R,)`. anchor (array): Coordinates of anchors. Its shape is :math:`(R, 4)`. img_size (tuple of ints): A tuple :obj:`height, width`, which contains image size after scaling. scale (float): The scaling factor used to scale an image after reading it from a file. Returns: array: An array of coordinates of proposal boxes. Its shape is :math:`(S, 4)`. :math:`S` is less than :obj:`self.n_test_post_nms` in test time and less than :obj:`self.n_train_post_nms` in train time. :math:`S` depends on the size of the predicted bounding boxes and the number of bounding boxes discarded by NMS. """ # NOTE: when test, remember # faster_rcnn.eval() # to set self.traing = False if self.parent_model.training: n_pre_nms = self.n_train_pre_nms # 12000 n_post_nms = self.n_train_post_nms # 经过 NMS 后有2000个 else: n_pre_nms = self.n_test_pre_nms # 6000 n_post_nms = self.n_test_post_nms # 经过NMS 后有300个 # Convert anchors into proposal via bbox transformations. # 将 bbox 转换为近似 ground_truth 的 anchor(即rois) roi = loc2bbox(anchor, loc) # Clip predicted boxes to image. roi[:, slice(0, 4, 2)] = np.clip( roi[:, slice(0, 4, 2)], 0, img_size[0]) roi[:, slice(1, 4, 2)] = np.clip( roi[:, slice(1, 4, 2)], 0, img_size[1]) # Remove predicted boxes with either height or width < threshold. min_size = self.min_size * scale # 16 hs = roi[:, 2] - roi[:, 0] # rois 的宽 ws = roi[:, 3] - roi[:, 1] # rois 的高 # 确保 rois 的长宽大于最小阈值 keep = np.where((hs >= min_size) & (ws >= min_size))[0] roi = roi[keep, :] # 对剩下的ROIs进行打分(根据 region_proposal_network 中 rois 的预测前景概率) score = score[keep] # Sort all (proposal, score) pairs by score from highest to lowest. # Take top pre_nms_topN (e.g. 6000). # 将 score 拉伸并逆序(从高到低) 排序 order = score.ravel().argsort()[::-1] if n_pre_nms > 0: order = order[:n_pre_nms] roi = roi[order, :] score = score[order] # Apply nms (e.g. threshold = 0.7). # Take after_nms_topN (e.g. 300). # unNOTE: somthing is wrong here! # TODO: remove cuda.to_gpu keep = nms( torch.from_numpy(roi).cuda(), torch.from_numpy(score).cuda(), self.nms_thresh) if n_post_nms > 0: keep = keep[:n_post_nms] roi = roi[keep.cpu().numpy()] return roi ```(需要再组织一下思路, 看看如何能更加精简地将接下来的工具函数讲解得更加清楚) 未完待续…
